Lunar tides are a fascinating natural phenomenon that occur due to the gravitational pull exerted by the Moon on the Earth. This celestial relationship creates a rhythmic ebb and flow of ocean waters, significantly influencing marine ecosystems and coastal environments. Understanding lunar tides not only enhances our appreciation for the natural world but also provides valuable insights into various scientific fields, including astronomy, oceanography, and environmental science.
The concept of lunar tides has intrigued humanity for centuries. Ancient civilizations were keen observers of the night sky and recognized the connection between the Moon's phases and the changing tides. The ancient Greeks, for instance, attributed the power of the tides to the gods, while Polynesian navigators relied on their knowledge of lunar cycles for navigation across vast oceans. In modern times, we have developed a deeper scientific understanding of how the gravitational forces from celestial bodies influence our planet.
Today, the study of lunar tides is crucial for various practical applications, such as predicting tidal patterns for fishermen, shipping industries, and coastal management. As we delve deeper into the complexities of lunar tides, we uncover the intricate interplay between celestial mechanics and Earth’s ecosystems. In this article, we will explore the fundamental aspects of lunar tides, their effects on our environment, and the science behind this captivating phenomenon.
What Causes Lunar Tides?
Lunar tides are primarily caused by the gravitational forces exerted by the Moon and, to a lesser extent, the Sun. When the Moon’s gravitational pull is stronger on one side of the Earth, it causes water to bulge outward, creating a high tide. Conversely, on the opposite side, the gravitational force is weaker, resulting in a low tide. This interplay creates a cycle of rising and falling tides experienced by coastlines around the world.
How Do Lunar Phases Affect Tides?
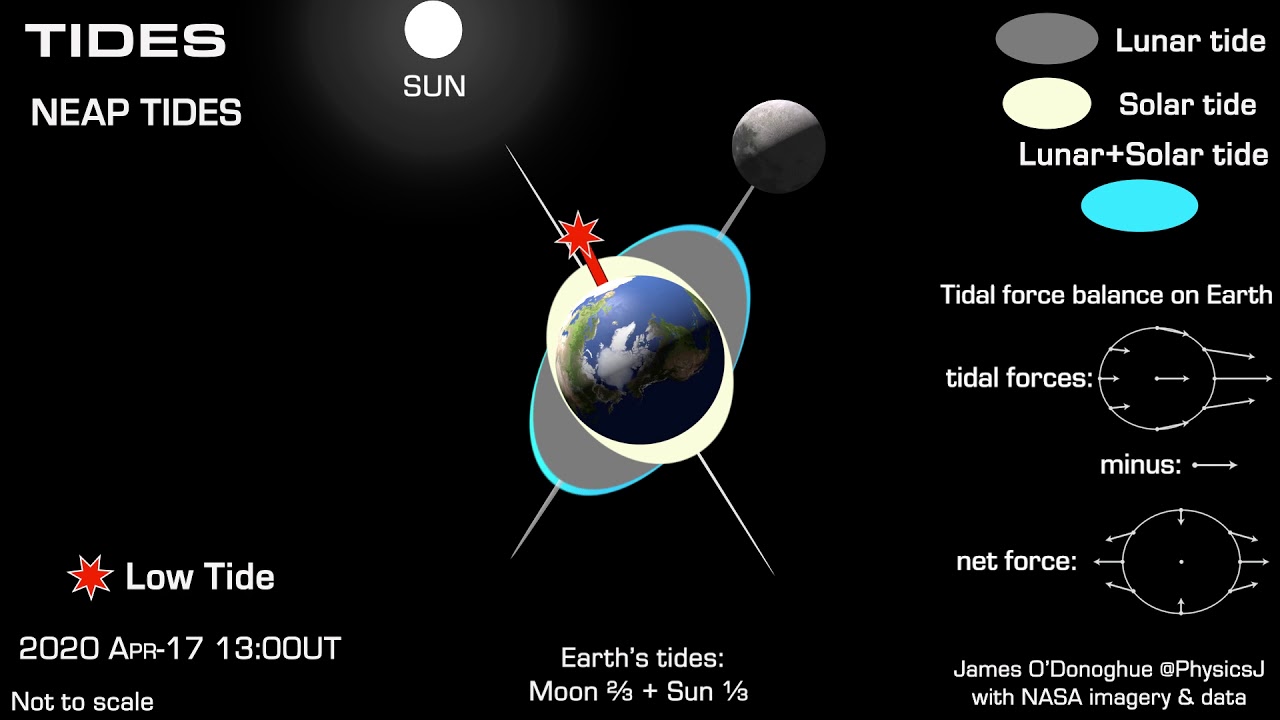
The phases of the Moon play a significant role in the intensity and timing of lunar tides. During a full moon or new moon, the Sun, Earth, and Moon align, resulting in higher high tides and lower low tides, known as spring tides. Conversely, during the first and third quarters of the Moon, the Sun and Moon are at right angles to each other, leading to lower high tides and higher low tides, known as neap tides.
What Are the Different Types of Tides?
- Diurnal Tides: These tides consist of one high tide and one low tide each lunar day, commonly observed in regions like the Gulf of Mexico.
- Semidiurnal Tides: This type includes two high tides and two low tides each lunar day, typical along the Atlantic coast of the United States.
- Mixed Tides: Mixed tides feature characteristics of both diurnal and semidiurnal tides, resulting in varying heights of tides throughout the day.
How Do Lunar Tides Impact Marine Life?
The rhythmic rise and fall of lunar tides are essential for the survival of numerous marine species. Many organisms, such as crabs, mollusks, and fish, rely on tidal movements for feeding, reproduction, and migration. For example, certain fish species spawn during specific tidal phases, ensuring the survival of their offspring by synchronizing their reproductive cycles with the optimal conditions provided by the tides.
What Role Do Lunar Tides Play in Coastal Environments?
Lunar tides are critical in shaping coastal environments. They help to transport nutrients, sediments, and pollutants, influencing the health of estuaries and coastal ecosystems. The regular movement of tides also creates habitats for various species, such as salt marshes and tidal flats, which serve as nurseries for young fish and other marine life.
Can Lunar Tides Affect Weather Patterns?
While lunar tides do not directly influence weather patterns, they can have indirect effects. The movement of water caused by tides can influence local climates, particularly in coastal areas. For instance, the temperature of coastal waters can affect atmospheric conditions, leading to changes in wind patterns and precipitation.
How Are Lunar Tides Measured?
Scientists measure lunar tides using tide gauges and satellite altimetry. Tide gauges are devices installed along coastlines that record water levels over time, providing valuable data for tidal predictions. Satellite altimetry, on the other hand, uses satellite technology to measure the height of the ocean's surface, allowing scientists to gather global tidal data and analyze patterns over larger areas.
What is the Future of Lunar Tides Research?
The study of lunar tides continues to evolve as technology advances. Researchers are exploring the potential impacts of climate change on tidal patterns, such as rising sea levels and altered tidal ranges. Additionally, understanding the effects of human activities, like coastal development and pollution, on lunar tides is crucial for protecting marine ecosystems and ensuring sustainable management of coastal resources.
In conclusion, lunar tides are a remarkable manifestation of the gravitational relationship between the Earth and the Moon. They play a vital role in shaping our oceans, influencing marine life, and impacting coastal environments. As we continue to study these dynamic systems, we gain valuable insights that can help us better understand and protect our planet's intricate ecosystems.
You Might Also Like
Charming Combinations: Cute Outfits With ShoesUnveiling The World Of Stylish Outfits: A Fashion Journey
Jeff Dunham: The Ventriloquist Who Captivated America
Understanding The Purpose Of Walk-In Ovens
Discovering The World Of Lenatheplugxx
Article Recommendations
- David Hefner
- Diddy And Justin Bieber
- Kim Erome
- Conell Twins
- Who Is Morgan Freemans Partner
- Kim Nam Gil
- Sadie Mckenna Nudes Leaked
- Owen Wilson Death
- Hd Moviehubin
- Kilmer Top Gun